A road to be a secure dev - From 0 to Kevin!
“There is no safe system”. As a developer, we are the first line of defense to produce safe systems. How can we learn to write secure code? And, even if we know how to write it, is there a way to write the code in a way that prevents failures and weaknesses to appear?
This article is about how can we achieve to be a secure developer. It will give an overview of the road to follow in order to write secure code. It defines different steps and actions. You will find a base for a maturity model assessment for
It comes from discussions we had with 0xbde on this subject at Software Crafters Paris.
Before beginning
As you can have security without quality, a necessary condition is to write quality code. You need to master techniques which will help you produce better software which is maintainable; auditable and clean. To do so, you will need to master TDD and simple design.
If you are looking for more information, you should have a look at the craft community.
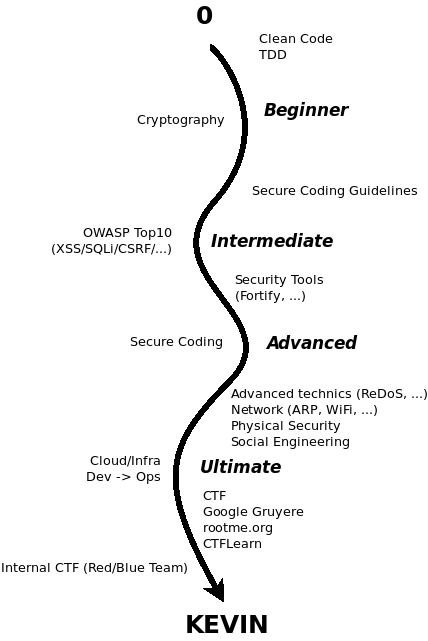
Level 1: Beginner
In this level, you need to understand key concepts in security. The first on is cryptography. Cryptography can be complex. You have to understand the difference between to crypt and to sign, what is symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, what makes an algorithm secure, which one is secure and how to use it in a way that it works. One important point is to not write yourself such an algorithm as it is a hard task. Know your limits and know when you need to search for some help.
Next step is to read and follow secure coding guidelines. Nowadays, every language, frameworks, servers, applications, companies, … publish those guidelines. It serves as a checklist and indications on how to write secure code. A lot of weaknesses come from badly configured systems or tools used in an unsafe way.
Level 2: Intermediate
In level 2, you will start to go one step further into security. You will discover basics techniques that opponents use to find weaknesses in your system.
For Web developers, a classical way to start is the OWASP Top 10. It lists the main security risks associated with web applications. There are also Top 10 mobile, cloud, …
From that kind of attacks, you learn how to protect your applications. There are simple techniques and checklists that you can follow in order to write secure code. That’s the foundation of Secure Coding. It is a way of writing applications to prevent security bugs from appearing.
Some tools are used to help people detect and test applications for finding security bugs. You can start to use tools like OWASP ZAP, SQLMap, … and integrate them in your CI/CD.
Level 3: Advanced
If you are at the Intermediate level, you have a good basics understanding of the security. The next level focuses on more advanced techniques that not so many people know about.
OWASP Top 10 is associated with a list of attacks aiming web applications. In the advanced level, a developer will have to increase his field of understanding by looking at more advanced techniques (ReDoS, Time Attack, …). He will also have to read about other things like social engineering, physical security, … And understand in which way it can harm his application. A broader and deeper approach.
One important part of the security is network and infrastructure. With the cloud, developers seem to have the possibility to “replace” ops. However, they will have to understand it and master the security parts of building network and servers.
Level 4: Ultimate
In the ultimate part, you will try to act more as an opponent. You will try to break applications. You can find CTF which are good exercises to discover new weaknesses and way to defeat a system.
You can organize internal CTF between teams to train them (Blue/Red Team).
You can also register to bug bounties programs to test your skills on real applications.
The road to being a secure dev is a long one.